Extracting Tags from Log Data
Overview
The Extract Tags rule allows you to parse and enrich log data by extracting specific portions of the log message and converting them into tags (key-value pairs). This enables you to capture dynamic attributes—like user IDs, session tokens, request IDs, or other contextual details—from unstructured log lines without manually updating your code or logs.
By selecting an exemplar log line and highlighting variable parts, you instruct the system to generate a regular expression that identifies these segments. You can then assign meaningful tag names to the extracted values. These tags are automatically added to the telemetry data, allowing for richer querying, filtering, and analysis of your logs.
What Does This Rule Do?
When logs flow through the pipeline, the Extract Tags rule:
- Identifies Matches: Uses a generated regex pattern to identify and extract variable portions of each log line.
- Assigns Tags: Maps each extracted portion to a user-defined tag name, effectively turning raw string data into structured attributes.
- Merges Tags: Incorporates these new tags into the existing set of log attributes. The merge strategy (insert, update, or upsert) controls how these extracted tags interact with pre-existing attributes.
This process transforms raw, unstructured log messages into richer, more queryable data, improving the observability and debugging experience.
Key Features
- No-Code Tag Extraction: Just pick an example log and highlight the parts you care about. The UI generates a suitable regex and handles the extraction.
- Customizable Tags: Assign human-readable tag names to the extracted values, making logs easier to search and correlate.
- Flexible Merge Strategies: Choose how new tags interact with existing attributes:
- Insert: Add new tags only if they don’t already exist.
- Update: Replace existing tags if they share the same name.
- Upsert: If a tag exists, update it; otherwise, create it.
- Conditional Application: Apply the rule selectively based on conditions. For example, only extract tags from logs originating from certain services or environments.
Options and Parameters
Example:
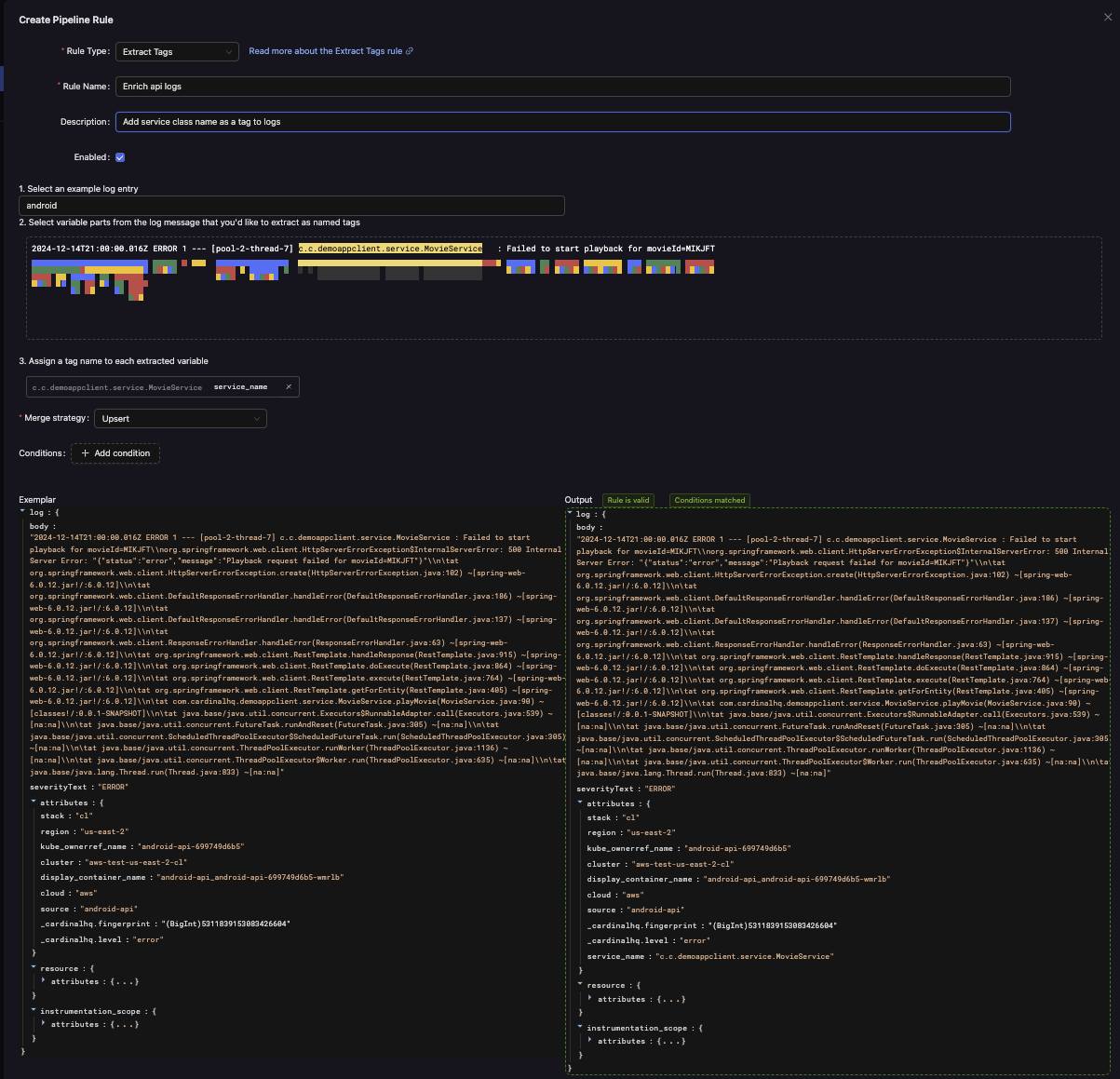
Exemplar Log Selection
- Choose a Sample Log: Begin by selecting a representative log entry from your telemetry.
- Highlight Variables: Using the UI, highlight portions of the log message that represent dynamic values (e.g., session IDs, request times, or user names).
The system generates a regex pattern that can extract these highlighted parts from similar logs.
Assigning Tag Names
After highlighting the variables, give each extraction a tag name. For instance, if you highlight user123 in a GET /home user123, you might label it as user_id. Now every log that matches this pattern will have user_id = "user123" (or the appropriate extracted value) added to its attributes.
Merge Strategy
Determine how extracted tags integrate with existing attributes:
- Insert: Only create new tags if they don’t exist. Do not overwrite existing tags.
- Update: Overwrite the value of any existing tag if one is found with the same name.
- Upsert (Default): If the tag exists, update it; if not, create it. This ensures your data remains current without losing existing information.
Conditions (Optional)
Add conditions to restrict when tags are extracted. For example, apply tag extraction only to logs from a specific service.name or environment. If conditions aren’t met, the extraction step is skipped, and the logs pass through unchanged.
Example Configuration
Goal: Extract a user ID and request path from a log line, and tag logs only if they come from the frontend-service.
Steps:
-
Select an Exemplar Log:
2024-04-12T10:23:47Z GET /home user123 -
Highlight Variables:
- Highlight
/homeas the request path. - Highlight
user123as the user ID.
The UI generates a regex to match similar patterns.
- Name the Tags:
request_path = /homeuser_id = user123
-
Set Merge Strategy: Choose
upsertto update existing tags if present, or insert them if they don’t exist. -
Conditions:
attributes[“service.name”] = “frontend-service”Only extract these tags for logs from frontend-service.
Result:
Logs from frontend-service now include request_path and user_id tags, making them easier to query and analyze. Logs from other services pass through unchanged.
Testing and Verification
- Validate Regex and Tags: Use the provided UI and sandbox to ensure that the regex accurately captures the desired variables from sample logs.
- Adjust Conditions: If your initial conditions are too broad or too narrow, refine them to achieve the right balance.
- Monitor Results: Check queries and dashboards to verify that the new tags improve log navigation and analysis.
Summary
The Extract Tags rule transforms unstructured log messages into rich, structured data by programmatically identifying and tagging variable components. This improves the usefulness of your logs, enabling more effective filtering, alerting, and visualization. By adding tags based on exemplar logs, you gain finer control over your telemetry and can derive greater insights with minimal upfront effort.